データベース処理遅延に対処するための「パフォーマンスログ」を採取する方法:SQL Serverトラブルシューティング(37)(1/2 ページ)
本連載は、「Microsoft SQL Server」で発生するトラブルを「どんな方法で」「どのように」解決していくか、正しい対処のためのノウハウを紹介します。今回は、「処理遅延の対処に役立てるパフォーマンスログの採取方法」を説明します。
本連載では、「Microsoft SQL Server(以下、SQL Server)」で発生するトラブルについて、「なぜ起こったか」の理由とともに具体的な対処方法を紹介していきます。
前回は、データベースの処理遅延を対処するために把握すべき、3つの項目を解説しました。今回はその具体的な取得情報の1つである「パフォーマンスログ」の採取方法を紹介します。
パフォーマンスログとは何か
パフォーマンスログは、Windows標準の「Windows パフォーマンス モニター」を使って採取する、Windows ServerやSQL Serverの動作状況を記録した情報です。採取したパフォーマンスログによって、データベースの処理遅延に何が影響を与えていたのかを推測できます。
パフォーマンスログを保存しておくには、明示的な「採取設定」が必要となります。そもそも採取の設定がされておらず、処理遅延の状況も再現できない場合には、パフォーマンスログを参照した調査ができません。まず、この設定を行っておきましょう。
パフォーマンスログの採取方法
パフォーマンスログは、Windows パフォーマンス モニターから「データコレクターセット」を作成することで採取できます。手順は以下の通りです。
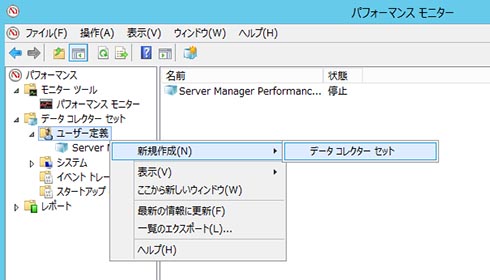
- Windows パフォーマンス モニターで、「データコレクターセット」→「ユーザー定義」を選択し、「新規作成」から新しいデータコレクターセットの作成ウィザードを開く(図1)
- 「手動で作成する」→「次へ」→「データログを作成する/パフォーマンスカウンター」にチェックを入れる
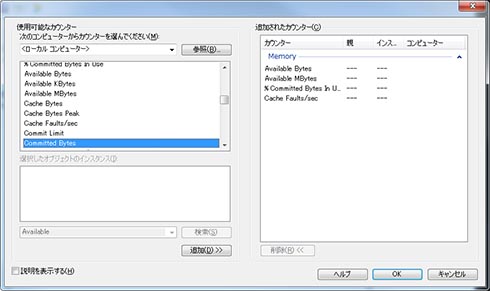
- 必要な「パフォーマンスカウンター」を追加する(図2)
- 「データの保存先」と「実行ユーザー」を指定し、データコレクターセットを作成する
手順(3)で作業する「パフォーマンスカウンター」は、CPU使用率やメモリ使用量といった、採取する情報ごとの項目のことです。テンプレートも幾つか用意されていますが、SQL Serverの管理を明確に考慮したテンプレートは今のところないようです。少し大変ですが、手動で追加しましょう。SQL Serverのトラブルシューティングを目的とする、筆者推奨のパフォーマンスカウンターは以下の通りです(表1)。
| オブジェクト名 | カウンター名 |
|---|---|
| Memory | % Committed Bytes In Use |
| Available Bytes | |
| Available MBytes | |
| Cache Faults/sec | |
| Committed Bytes | |
| Free System Page Table Entries | |
| Page Faults/sec | |
| Page Reads/sec | |
| Pages/sec | |
| Pool Nonpaged Bytes | |
| Pool Paged Bytes | |
| Transition Faults/sec | |
| Paging File | % Usage |
| % Usage Peak | |
| PhysicalDisk | Avg. Disk Queue Length |
| Avg. Disk sec/Read | |
| Avg. Disk sec/Write | |
| Current Disk Queue Length | |
| Disk Read Bytes/sec | |
| Disk Write Bytes/sec | |
| Process | % Privileged Time |
| % Processor Time | |
| Handle Count | |
| Page Faults/sec | |
| Private Bytes | |
| Thread Count | |
| Working Set | |
| Working Set - Private | |
| Processor | % Idle Time |
| % Privileged Time | |
| % Processor Time | |
| % User Time | |
| Interrupts/sec | |
| Processor Information | % Processor Performance |
| Parking Status | |
| Processor Frequency | |
| System | Context Switches/sec |
| Processes | |
| Processor Queue Length | |
| Threads | |
| Threads | Context Switches/sec |
| SQLServer:Access Methods | Forwarded Records/sec |
| FreeSpace Scans/sec | |
| Full Scans/sec | |
| Index Searches/sec | |
| Page Splits/sec | |
| Scan Point Revalidations/sec | |
| Workfiles Created/sec | |
| Worktables Created/sec | |
| SQLServer:Buffer Manager | Buffer cache hit ratio |
| Checkpoint pages/sec | |
| Lazy writes/sec | |
| Page life expectancy | |
| Page lookups/sec | |
| Page reads/sec | |
| Page writes/sec | |
| Readahead pages/sec | |
| SQLServer:Cursor Manager by Type | Cursor Requests/sec |
| SQLServer:Databases | Data File(s) Size (KB) |
| Log File(s) Size (KB) | |
| Log File(s) Used Size (KB) | |
| Log Flush Wait Time | |
| Log Flush Waits/sec | |
| Log Growths | |
| Transactions/sec | |
| SQLServer:General Statistics | Logins/sec |
| Logouts/sec | |
| Processes blocked | |
| User Connections | |
| SQLServer:Latches | Average Latch Wait Time (ms) |
| Latch Waits/sec | |
| Total Latch Wait Time (ms) | |
| SQLServer:Locks | Average Wait Time (ms) |
| Lock Timeouts (timeout > 0)/sec | |
| Lock Wait Time (ms) | |
| Lock Waits/sec | |
| Number of Deadlocks/sec | |
| SQLServer:Memory Manager | Free Memory (KB) |
| Memory Grants Pending | |
| Target Server Memory (KB) | |
| Total Server Memory (KB) | |
| SQLServer:Plan Cache | Cache Hit Ratio |
| SQLServer:SQL Errors | Errors/sec |
| SQLServer:SQL Statistics | Auto-Param Attempts/sec |
| Batch Requests/sec | |
| Failed Auto-Param/sec | |
| SQL Attention rate | |
| SQL Compilations/sec | |
| SQL Re-Compilations/sec | |
| SQLServer:Wait Statistics | Lock waits |
| Log write waits | |
| Network IO waits | |
| Non-Page latch waits | |
| Page IO latch waits | |
| Page latch waits | |
| Wait for the worker | |
| SQLServer:Workload Group Stats | Active requests |
| Blocked tasks | |
| CPU usage % | |
| Queued requests | |
| *名前付きインスタンスの場合は、「SQLServer:**」ではなく「MSSQL$<インスタンス名>:**」というオブジェクト名になります | |
関連記事
 「SQL Server 2016」に搭載される新たなセキュリティ対策を追う
「SQL Server 2016」に搭載される新たなセキュリティ対策を追う
パブリックプレビューが公開されているマイクロソフトのRDB次期版「SQL Server 2016」。特徴の1つとするセキュリティ対策機能のポイントと目指すところをキーパーソンに聞いた。 そもそも、リレーショナルデータベースとは何か?
そもそも、リレーショナルデータベースとは何か?
データベースを基礎から勉強し理解を深めていくことは簡単なことではありません。本連載では、データベースに対するハードルを少しでも低くするために、初心者の方に必要なデータベースの基本から、障害対策やチューニングといった実践に即した内容までを幅広く解説していきます。今回は、データベースの役割と、それを管理するソフトウェアであるDBMSの基本機能について解説します。【更新】 データの登録を行うINSERT文
データの登録を行うINSERT文
 複数の条件を指定してSELECT文を実行する
複数の条件を指定してSELECT文を実行する
前回は、SELECT文の初歩の初歩を解説しました。今回は、複数の条件を指定して、目的のデータを取り出す方法を解説します(編集部) Oracle運用の基本「ログ」を理解しよう
Oracle運用の基本「ログ」を理解しよう
本連載では、Oracle Database運用の鍵となるトラブル対処法について紹介していきます。第1回、第2回では情報収集の要となるログについて見ていきます。ログの出力情報は10gと11gとでは大きく異なる点がありますので、それぞれについても確認しておきましょう。
Copyright © ITmedia, Inc. All Rights Reserved.